Histology 101: Exploring Special Stains Beyond H&E
- Eghosa Arovo

- Mar 20, 2025
- 3 min read
While Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining provides foundational insights into tissue architecture, special stains are invaluable for highlighting specific tissue components, aiding in precise diagnoses. This article delves into some of the primary special stains used in histology, including Perls' Prussian Blue, Reticulin, Sirius Red, Masson's Trichrome, and Verhoeff's Elastic Stain, along with honorable mentions of other notable staining techniques.www.slideshare.net
Perls' Prussian Blue Stain
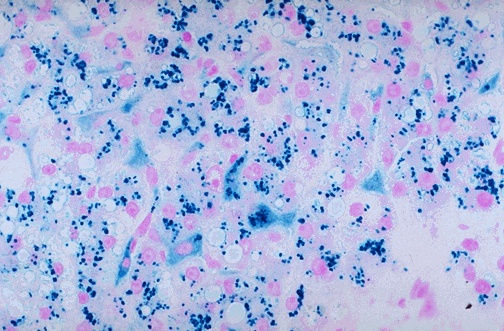
Purpose: Detects ferric (Fe³⁺) iron deposits in tissues.https://histologyresearchcorefacility.web.unc.edu+2Leica Biosystems+2Wikipedia
Application: Commonly used to identify hemosiderin, an iron-storage complex, especially in conditions like hemochromatosis and hemosiderosis. In liver biopsies, it helps assess iron accumulation within hepatocytes and Kupffer cells. Leica Biosystems+4PMC+4https://histologyresearchcorefacility.web.unc.edu
Mechanism: Tissue sections are treated with potassium ferrocyanide and hydrochloric acid, resulting in the formation of an insoluble blue pigment where ferric iron is present. Wikipedia
Reticulin Stain

Purpose: Highlights reticular fibers composed predominantly of type III collagen.https://histologyresearchcorefacility.web.unc.edu
Application: Essential in liver histopathology to assess the architecture of hepatic lobules and identify abnormalities like fibrosis or neoplasms. Wikipedia
Mechanism: Utilizes silver impregnation techniques, where reticular fibers reduce silver nitrate to visible metallic silver, appearing as black or dark brown fibers against a light background.
Sirius Red Stain
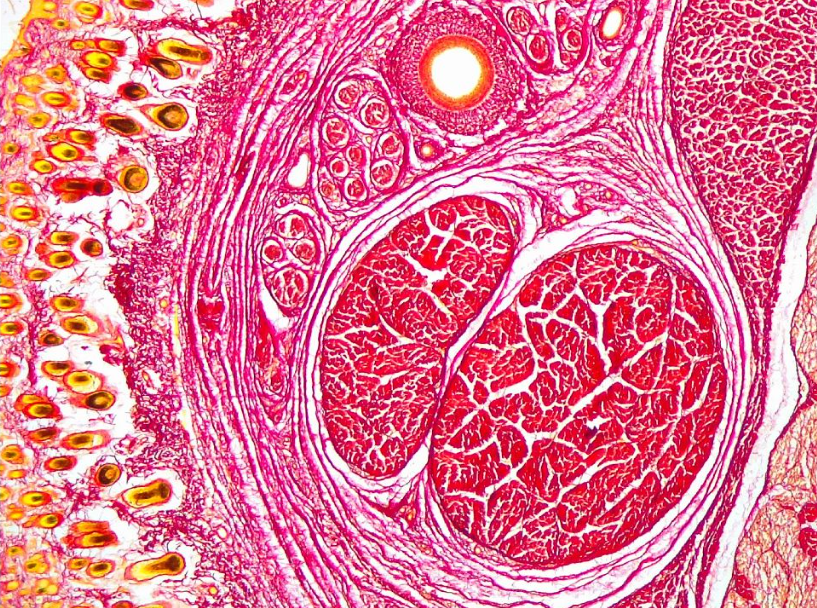
Purpose: Specifically stains collagen fibers.
Application: Used to evaluate fibrosis in tissues such as the liver, where collagen deposition indicates the extent of fibrotic changes.
Mechanism: Sirius Red binds to collagen fibers, staining them red. When viewed under polarized light, collagen appears as bright orange-red fibers, enhancing the contrast and aiding in quantification.
Masson's Trichrome Stain
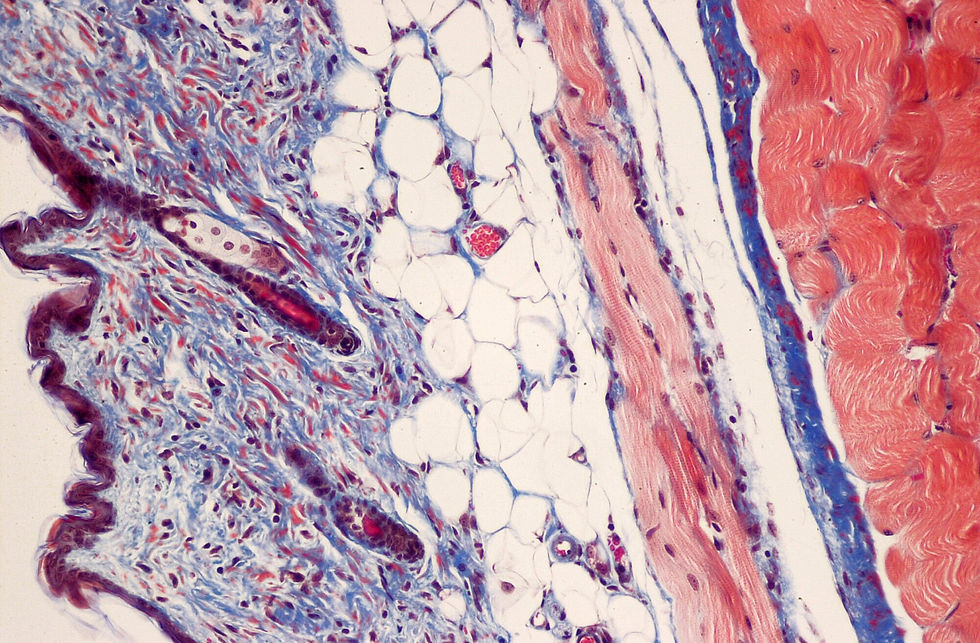
Purpose: Differentiates between collagen and muscle fibers.Wikipedia+6Wikipedia+6Wikipedia+6
Application: Assists in identifying increases in collagenous tissue, such as in liver cirrhosis, and distinguishing tumors arising from muscle cells and fibroblasts. Wikipedia
Mechanism: Involves sequential application of dyes: Weigert's iron hematoxylin stains nuclei black; Biebrich scarlet-acid fuchsin stains cytoplasm, muscle, and keratin red; and aniline blue or light green stains collagen fibers blue or green, respectively.
Verhoeff's Elastic Stain (EVG)
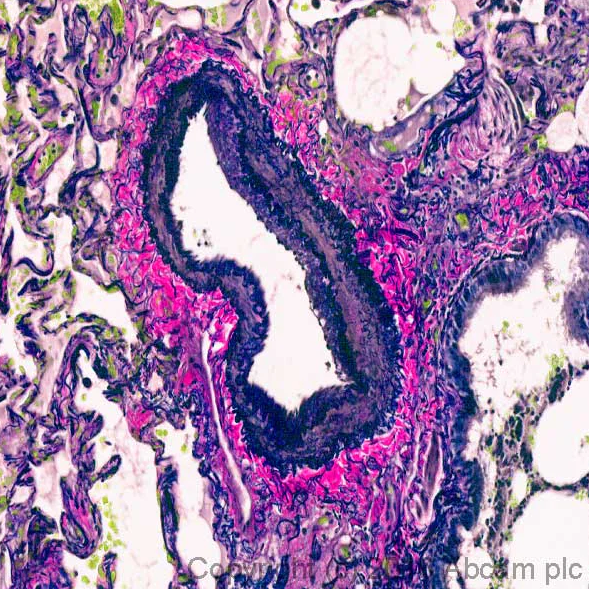
Purpose: Visualizes elastic fibers in tissues.
Application: Evaluates vascular diseases by highlighting elastic laminae in arteries and veins, aiding in the assessment of conditions like arteriosclerosis. Wikipedia+1Wikipedia+1
Mechanism: Elastic fibers have a strong affinity for the iron-hematoxylin complex formed by the reagents in the stain and will hence retain dye longer than other tissue elements. This allows elastic fibers to remain stained while the remaining tissue elements are decolorized. Wikipedia
Honorable Mentions
Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) Stain: Highlights structures containing a high proportion of carbohydrates such as glycogen, glycoproteins, and proteoglycans. Often used to stain kidney biopsies, liver biopsies, certain glycogen storage diseases in striated muscles, and suspected fungal infections. Leica Biosystems+1www.slideshare.net+1
Alcian Blue Stain: Identifies acid mucopolysaccharides and acidic mucins. Excessive amounts of non-sulfated acidic mucosubstances are seen in mesotheliomas, and certain amounts occur normally in blood vessel walls but increase in early lesions of atherosclerosis. https://histologyresearchcorefacility.web.unc.edu+3Leica Biosystems+3WebPath+3
Ziehl-Neelsen Stain: Detects acid-fast bacilli, notably Mycobacterium species responsible for tuberculosis. Acid-fast bacilli appear as bright red rods against a blue background. Leica Biosystems
Conclusion
Special stains are indispensable tools in histology, each tailored to reveal specific tissue components or pathogens. Their appropriate application enhances diagnostic accuracy and deepens our understanding of tissue pathology.www.slideshare.net+1Leica Biosystems
References
For expert histology services, including the application of these special stains, LabNexus is here to support your research needs. And don't forget to enter our monthly giveaway - we're giving away an iPad Air!
.png)


Comments